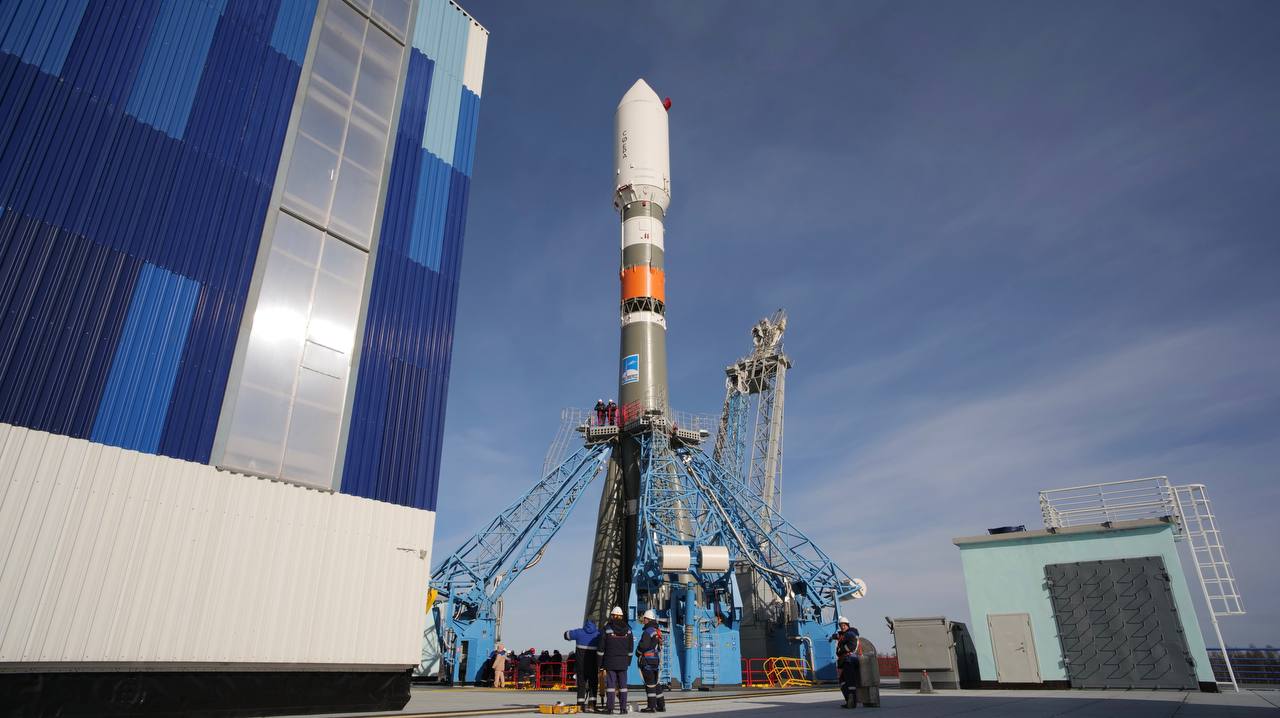

Launch
Russian Space Forces
Soyuz 2.1b/Fregat | Glonass-K1 No. 19
- Mission
- rocket
- Pad
- Agency
Mission
Glonass-K1 No. 19
Navigation
Medium Earth Orbit
Glonass-K are the third generation of satellite design for GLONASS satellite navigation system. GLONASS is a Russian space-based navigation system comparable to the similar GPS and Galileo systems. This generation improves on accuracy, power consumption and design life. Each satellite is unpressurized and weighs 935 kg, and has an operational lifetime of 10 years.
Status
To Be Determined
Current date is a placeholder or rough estimation based on unreliable or interpreted sources.
Pad
Location
Europe/Moscow
Plesetsk Cosmodrome, Russian Federation
Plesetsk Cosmodrome is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, about 800 km north of Moscow and approximately 200 km south of Arkhangelsk. Originally developed as an ICBM site for the R-7 missile, it also served for numerous satellite launches using the R-7 and other rockets. Its high latitude makes it useful only for certain types of launches, especially the Molniya orbits, so for much of the site's history it functioned as a secondary location, with most orbital launches taking place from Baikonur, in the Kazakh SSR. With the end of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became a foreign territory, and Kazakhstan charged $115 million usage fees annually. Consequently, Plesetsk has seen considerably more activity since the 2000s.
1680
0
Location Image

Rocket

Soyuz 2.1b Fregat
Soyuz-2, GRAU index 14A14, is the collective designation for the 21st-century version of the Russian Soyuz rocket. In its basic form, it is a three-stage carrier rocket for placing payloads into low Earth orbit. The first-stage boosters and two core stages feature uprated engines with improved injection systems, compared to the previous versions of the Soyuz. Digital flight control and telemetry systems allow the rocket to be launched from a fixed launch platform, whereas the launch platforms for earlier Soyuz rockets had to be rotated as the rocket could not perform a roll to change its heading in flight. The Soyuz 2.1b represents the latest development stage of the proven rocket. It uses the new RD-0124 engines in the first three stages, coupled with an improved injection system that significantly boosts the performance of the Soyuz. Furthermore, she wears a new, digital startup control system. This will allow the Soyuz 2.1b to carry around 1.2 tonnes more payload into low earth orbit compared to its predecessor.
Family: Soyuz
Variant: Fregat
Details
Min stage: 3
Max stage: 4m
Length: 46.3m
Diameter: 2.95
First Flight: Dec. 27, 2006
Total launch count: 25
Successful launches: 23
Failed launches: 2
Pending launches: 1
Consecutive successful launches: 9
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) capacity: 8200kg
Launch cost: US$80000000
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) capacity: 3250kg
Manufacturer
Progress Rocket Space Center
Commercial
RUS
Progress Rocket Space Centre, formerly known as TsSKB-Progress, is a space science and aerospace research company which is known for manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites. Most notably, Progress Rocket Space Centre is the manufacturer of Soyuz launch vehicles.
1996
CEO: Dmitry Baranov

Agency

Russian Space Forces
The Russian Space Forces are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Russia. Having been reestablished following August 1, 2015 merger between the Russian Air Force and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces after a 2011 dissolving of the branch. The Russian Space Forces were originally formed on August 10, 1992 and the creation of the Russian Armed Forces.
RUS
Type: Government
Details
Commander: Aleksandr Golovko
1992
Total launch count: 147
Successful launches: 139
Consecutive successful launches: 59
Failed launches: 8
Pending launches: 1


