
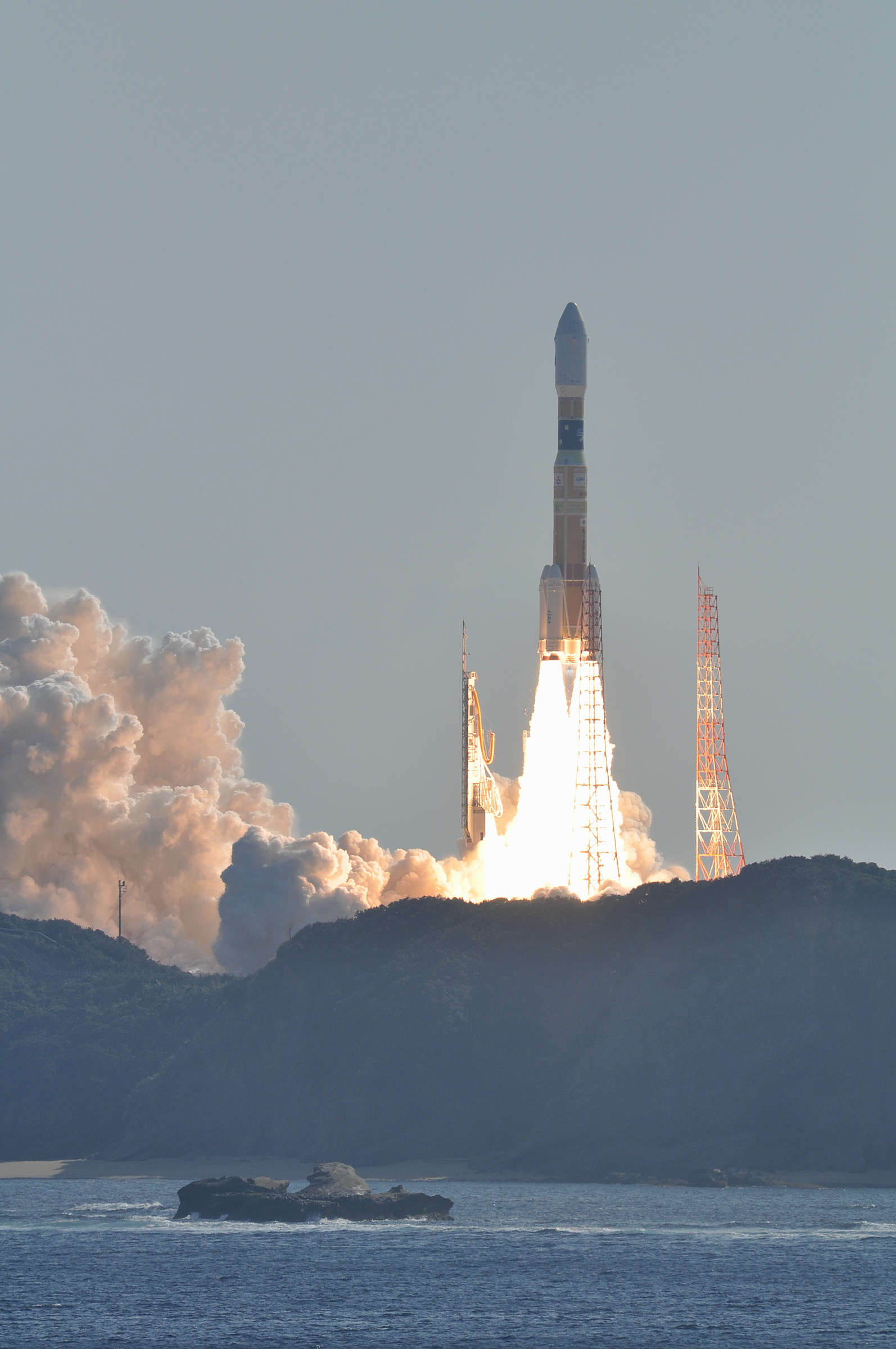
Launch
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
H3-22 | Michibiki 7 (QZS-7)
- Mission
- rocket
- Pad
- Agency
Mission
Michibiki 7 (QZS-7)
Navigation
Geostationary Transfer Orbit
QZSS (Quasi Zenith Satellite System) is a Japanese satellite navigation system operating from inclined, elliptical geosynchronous orbits to achieve optimal high-elevation visibility in urban canyons and mountainous areas. The navigation system objective is to broadcast GPS-interoperable and augmentation signals as well as original Japanese (QZSS) signals from a three-spacecraft constellation. The navigation system objective is to broadcast GPS-interoperable and augmentation signals as well as original Japanese (QZSS) signals from a three-spacecraft constellation in inclined, elliptical geosynchronous orbits.
Status
To Be Determined
Current date is a placeholder or rough estimation based on unreliable or interpreted sources.
Pad
Location
Asia/Tokyo
Tanegashima Space Center, Japan
The Tanegashima Space Center is the largest rocket-launch complex in Japan. It is located on the southeastern tip of Tanegashima, an island located south of Kyushu, an island and region and Japan. It was established in 1969 when the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) was formed, and is now run by JAXA. The activities that take place at TNSC include assembly, testing, launching, and tracking satellites, as well as rocket engine firing tests.
97
0
Location Image

Rocket

H3-22
The H3 Launch Vehicle is a Japanese expendable launch system. Each H3 booster configuration has a two-digit and a letter designation that indicates the features of that configuration. The first digit represents the number of LE-9 engines on the main stage, either "2" or "3". The second digit indicates the number of SRB-3 solid rocket boosters attached to the base of the rocket, and can be "0", "2" or "4". All layouts of solid boosters are symmetrical. The letter in the end shows the length of the payload fairing, either short "S" or long "L". For example, an H3-24L has two engines, four solid rocket boosters, and a long fairing, whereas an H3-30S has three engines, no solid rocket boosters, and a short fairing.
Details
Min stage: 2
Max stage: 2m
Length: 63.0m
Diameter: 5.27
First Flight: March 7, 2023
Total launch count: 6
Successful launches: 4
Failed launches: 2
Pending launches: 2
Launch cost: US$50000000
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) capacity: 5400kg
Manufacturer
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Commercial
JPN
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group. MHI's products include aerospace components, air conditioners, aircraft, automotive components, forklift trucks, hydraulic equipment, machine tools, missiles, power generation equipment, printing machines, ships and space launch vehicles. Through its defense-related activities, it is the world's 23rd-largest defense contractor measured by 2011 defense revenues and the largest based in Japan.
1884
President: Seiji Izumisawa
H-I, H-II, H-III
Kounotori | HTV



Agency

Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group. MHI's products include aerospace components, air conditioners, aircraft, automotive components, forklift trucks, hydraulic equipment, machine tools, missiles, power generation equipment, printing machines, ships and space launch vehicles. Through its defense-related activities, it is the world's 23rd-largest defense contractor measured by 2011 defense revenues and the largest based in Japan.
Details
President: Seiji Izumisawa
1884
H-I, H-II, H-III
Kounotori | HTV
Total launch count: 56
Successful launches: 54
Failed launches: 2
Pending launches: 10


