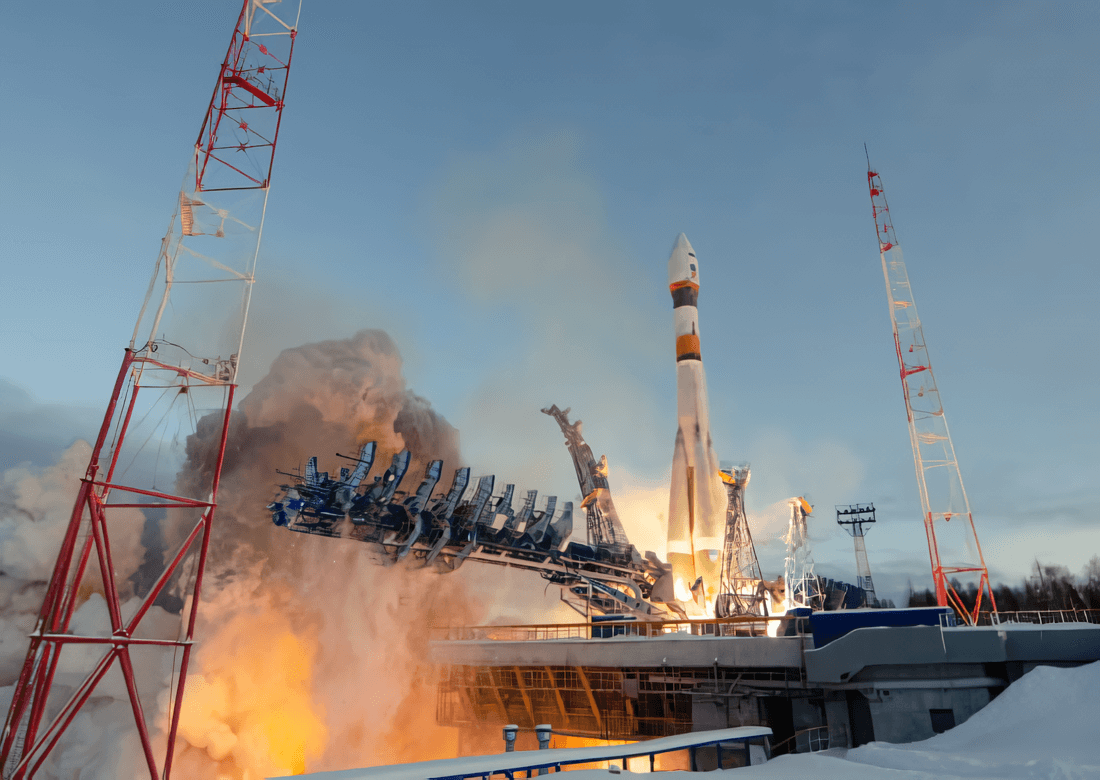
Launch
Russian Space Forces
Soyuz 2.1b | Kosmos 2573 (Bars-M No. 5?)
- Mission
- rocket
- Pad
- Agency
Mission
Kosmos 2573 (Bars-M No. 5?)
Government/Top Secret
Sun-Synchronous Orbit
Note: Payload identity uncertain, possibly Bars-M #5 or a similar satellite as the insertion orbit is similar. Bars-M is the second incarnation of the Bars project, which was started in the mid 1990ies to develop a successor for the Komtea class of area surveillance satellites. The original Bars project was halted in the early 2000s. In 2007, TsSKB-Progress was contracted for Bars-M, for which reportedly the Yantar-based service module was replaced by a new developed advanced service module. The Bars-M satellites feature an electro-optical camera system called Karat, which is developed and built by the Leningrad Optical Mechanical Association (LOMO), and a dual laser altimeter instrument to deliver topographic imagery, stereo images, altimeter data and high-resolution images with a ground resolution around 1 meter.
Status
Launch Successful
The launch vehicle successfully inserted its payload(s) into the target orbit(s).
Pad
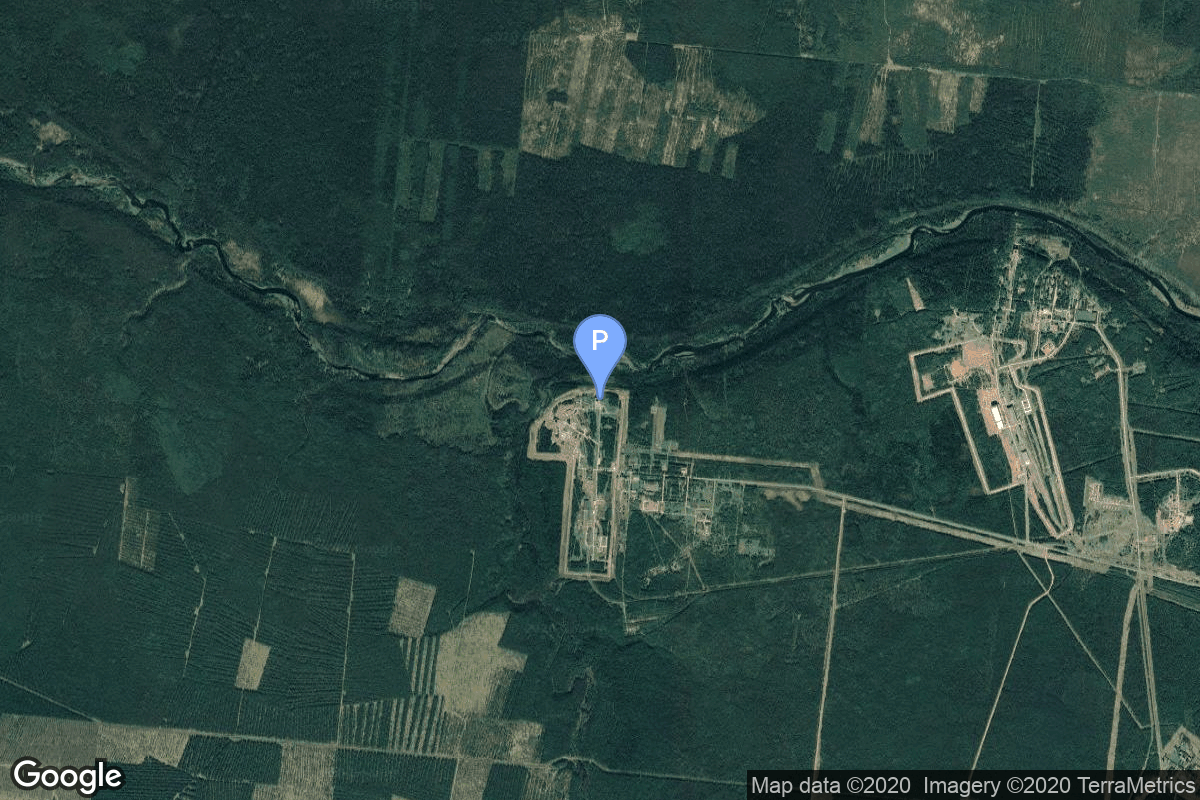
43/4 (43R)
RUS
Latitude: 62.92883
longitude: 40.457098
Map
Location
Europe/Moscow
Plesetsk Cosmodrome, Russian Federation
Plesetsk Cosmodrome is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, about 800 km north of Moscow and approximately 200 km south of Arkhangelsk. Originally developed as an ICBM site for the R-7 missile, it also served for numerous satellite launches using the R-7 and other rockets. Its high latitude makes it useful only for certain types of launches, especially the Molniya orbits, so for much of the site's history it functioned as a secondary location, with most orbital launches taking place from Baikonur, in the Kazakh SSR. With the end of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became a foreign territory, and Kazakhstan charged $115 million usage fees annually. Consequently, Plesetsk has seen considerably more activity since the 2000s.
1678
0
Location Image

Rocket

Soyuz 2.1b
Soyuz-2 is the 21st-century version of the Russian Soyuz rocket. In its basic form, it is a three-stage carrier rocket for placing payloads into low Earth orbit. The 2.1b version adds an upgraded engine (RD-0124) with improved performance to the second stage.
Family: Soyuz
Details
Min stage: 2
Max stage: 3m
Length: 46.3m
Diameter: 2.95
First Flight: July 26, 2008
Total launch count: 22
Successful launches: 22
Consecutive successful launches: 22
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) capacity: 8200kg
Launch cost: US$80000000
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) capacity: 3250kg
Manufacturer
Progress Rocket Space Center
Commercial
RUS
Progress Rocket Space Centre, formerly known as TsSKB-Progress, is a space science and aerospace research company which is known for manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites. Most notably, Progress Rocket Space Centre is the manufacturer of Soyuz launch vehicles.
1996
CEO: Dmitry Baranov

Agency

Russian Space Forces
The Russian Space Forces are a branch of the Russian Aerospace Forces, that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Russia. Having been reestablished following August 1, 2015 merger between the Russian Air Force and the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces after a 2011 dissolving of the branch. The Russian Space Forces were originally formed on August 10, 1992 and the creation of the Russian Armed Forces.
RUS
Type: Government
Details
Commander: Aleksandr Golovko
1992
Total launch count: 147
Successful launches: 139
Consecutive successful launches: 59
Failed launches: 8
Pending launches: 1


